The basic reasons for the reduction of micromotor efficiency
Efficiency is an important performance indicator of micromotors. The efficiency of micromotors with different numbers of poles is different. The efficiency of micromotors with high rotation speed is higher than that of micromotors with low rotation speed. Except for 2-pole micromotors, 4/6/8-pole micromotors have different efficiency. The lower the efficiency index of the micromotor, the lower the efficiency. Under the same power conditions, the speed and torque are inversely related. The higher the speed, the lower the torque.
For micromotors with the same torque, the higher the speed, the higher the efficiency. Slip is a parameter unique to micromotors. From the speeds of high-efficiency micromotors and ordinary micromotors, it can be found that the speed of high-efficiency motors is higher than that of ordinary micromotors. Micromotor, or the slip ratio is smaller. The micromotor slip is closely related to the rotor winding resistance. If the resistance is large, the slip ratio is large, and the rotor resistance loss is also large, resulting in low efficiency and small slip ratio.

So, what are the basic reasons that cause the efficiency of micromotors to decrease?
1. Micromotor stator has large copper loss
(1) The micromotor winding resistance is high: such as high wire resistivity or small wire diameter, uneven wire diameter, incorrect wiring or weak welding, etc.;
(2) Large stator current: such as other large losses, stator winding asymmetry, uneven stator and rotor air gap, less than normal number of turns, incorrect winding wiring, etc.
2. The micromotor rotor has large copper losses
(1) The micromotor rotor winding resistance is large: the resistivity of copper is large, there are pores or impurities in the aluminum rotor end ring, the material does not meet the requirements, the rotor is wrong, etc.;
(2) Large rotor flow: If the alloy rotor is made of ordinary aluminum, the rotor core is not stacked tightly, resulting in excessive rotor transverse current.
3. Micromotor has large iron loss
The silicon steel sheet of the micromotor is of poor quality or the wrong material, the stator core is poorly insulated, the core lamination pressure is high, the core sheet is short-circuited, etc.
4. Large mechanical loss
The bearing heats up and rotates inflexibly, the diameter of the bearing chamber is small, the lubrication quality is poor, the bore is swept, and the friction resistance is large.
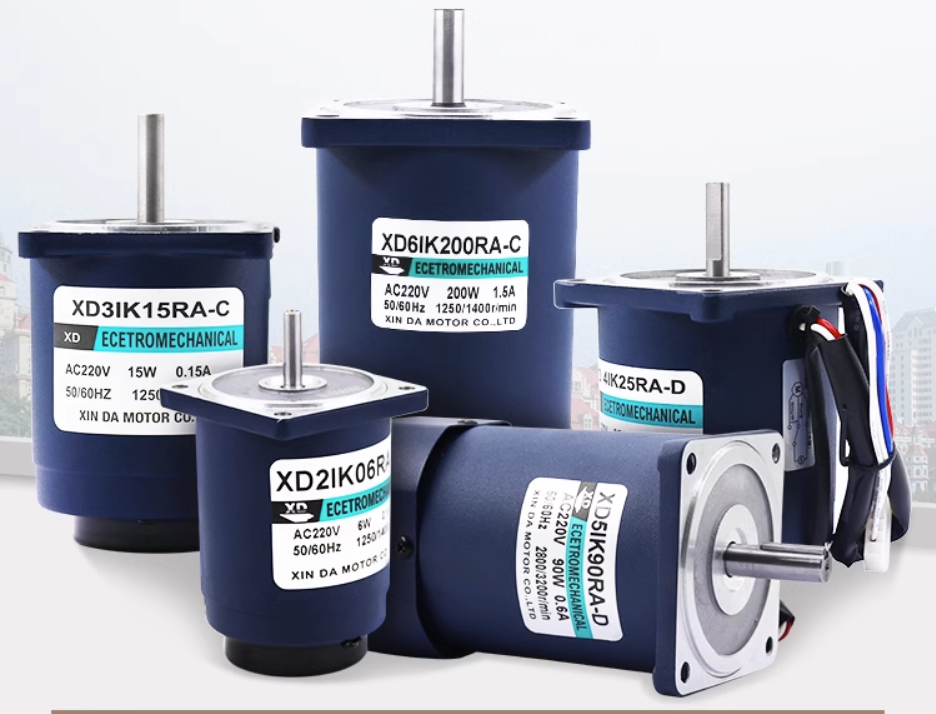


























 XINDA
XINDA