How to choose single-phase motor capacitor?
1. Why do we need to add capacitors to single-phase motors?
a. Two coils are energized at the same time. For single-phase asynchronous motors, there is only one AC current. What will happen when the stator wires A and B are connected at the same time (the coil is energized to generate a magnetic field, which attracts the rotor to rotate)? The rotor may rotate clockwise or counterclockwise. This kind of motor cannot be used in actual production.
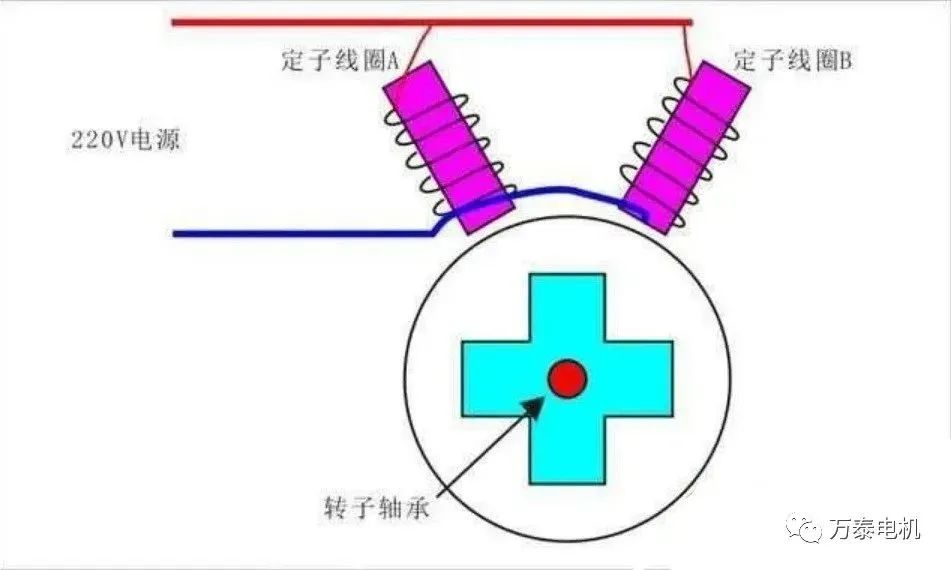
b. There is a sequence in which the two coils are powered.
Still looking at the motor model diagram above, if coil A is energized first and coil B is energized later, then the rotor must rotate counterclockwise. In the same way, if coil B is energized first and coil A is energized later, it will rotate clockwise. In this way, the direction of the motor is determined, and there will be no situation where it can be left or right.
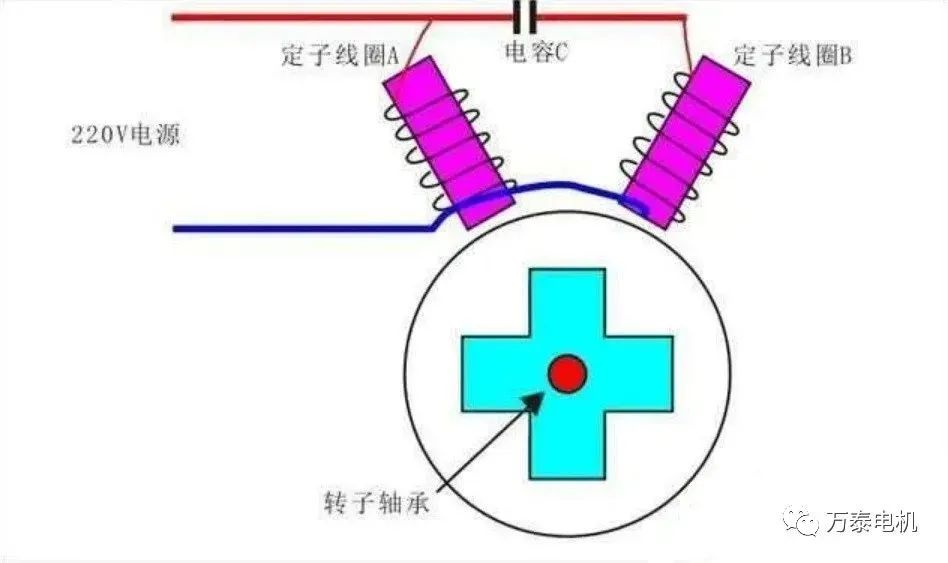
For alternating current, the current lead or lag is realized by inductor or capacitor. The motor itself is an inductor and can only be realized by capacitor. Although it is called a starting capacitor, this capacitor is mainly used to shift the phase, that is, to make the coil energized in a different order.
A single-phase motor cannot start normally by relying on the running winding alone. It is necessary to install a starting winding and then split the phase through the capacitor to help the motor start. In terms of design, some motors will disconnect the circuit between the starting winding and the capacitor through a centrifugal switch after starting, and only rely on the running winding to work. Some motors do not have a centrifugal switch. After the motor is started, the starting winding will serve as a secondary winding and capacitor to continue to help the motor operate normally.
Some motors also have a running capacitor installed on the basis of the starting capacitor, which is generally smaller than the starting capacitor. The purpose is to increase the motor torque and cooperate with the secondary winding to help the main winding complete the operation. In fact, this can also be understood as adding an extra starting capacitor inside the ordinary capacitor-operated motor.
2. How to choose the capacitor of a single-phase motor
The calculation formula of single-phase motor operating capacitance: GC=1950I/Ucos∮ (microfarad)
I: motor current
U: Single-phase power supply voltage
cos∮: power factor, taken as 0.75
1950: constant
If the single-phase power is 220Vrms, then GC=1950I/Ucos∮=1950P/(U^2)cos∮=1950*P/(220*220)*0.75≈0.03*P(uF)
where P is the motor power


























 XINDA
XINDA