How to quickly determine the direction of motor rotation
In the motor testing or initial design stage, the direction of motor rotation needs to be considered, and how to design the three-phase relationship of the windings affects the direction of motor rotation.

For a 6-pole 9-slot motor, the slot electrical angle is 3*360/9=120 degrees, so adjacent slots are adjacent phases. Lead wires to teeth 1, 2, and 3 in the figure, which are ultimately defined as ABC phases. We have calculated above that the electrical angle between 1, 2-2, 3-3, and 1 is 120 degrees, but we don't know whether it is a lead or a lag relationship.
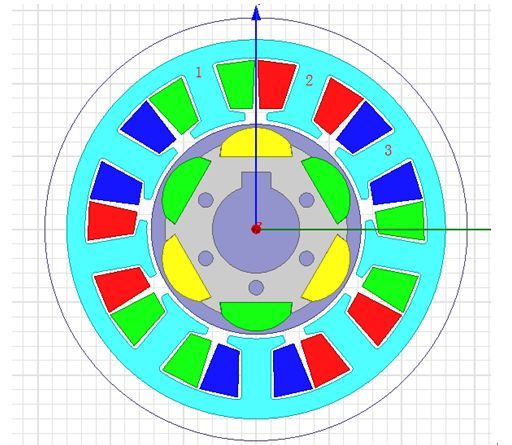
Figure 1 6-pole 9-slot motor model
If the motor rotates clockwise, you can observe the peak value of the back electromotive force. Tooth 1 reaches the peak first, then tooth 2, and then tooth 3. Then we can connect 1A 2B 3C, so the motor will rotate clockwise. The idea of this method is that the back electromotive force phase relationship of the motor corresponds to the power supply energizing the phase winding.
If the motor rotates counterclockwise, tooth 3 peaks first, then tooth 2, then tooth 1. So the wiring can be 3A 2B 1C, so the motor will rotate counterclockwise.
In fact, the direction of motor rotation is determined by the phase sequence . The phase sequence is the sequence of phases, not a fixed position, so it corresponds to the phase sequence of 123 teeth: ABC, CAB, BCA wiring method. In the above example, the rotation of the motor The directions are all clockwise. Corresponding to 123 teeth: CBA, ACB, BAC wiring mode motor rotates counterclockwise.
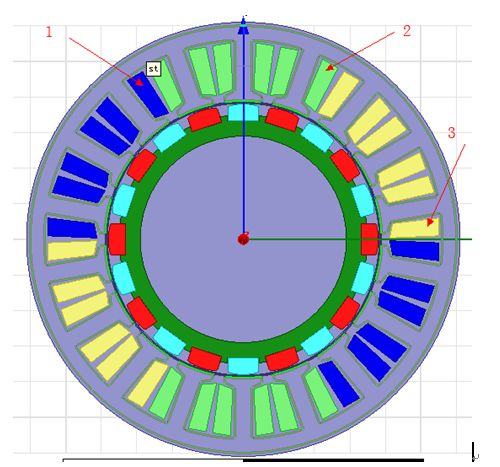
Figure 2 20-pole 18-slot motor model
This motor has 20 poles and 18 slots, and the unit motor corresponds to 10 poles and 9 slots. The slot electrical angle is 360/18*10=200°. According to the winding arrangement, the 1-2-3 windings are 3 slots apart, corresponding to a 600° electrical angle difference. The 600° electrical angle is the same as the 240° electrical angle, so the motor The angle between the 1-2-3 windings is 240°. Mechanically or physically (or in the picture above) the order of 1-2-3 is clockwise, but from an electrical angle 1-2-3 is arranged counterclockwise as shown below, because the electrical angle difference is 240 °.
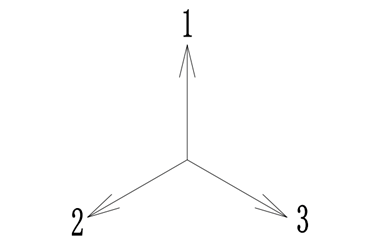
Figure 3 Electrical angle arrangement of windings
Therefore, if your power-on sequence is 1-2-3 at this time (the maximum magnetic potential sweeps through 1 first, then sweeps through 2, then sweeps through 3), and the direction of rotation of the magnetic field is counterclockwise, the motor will rotate counterclockwise. . When energizing in the 1-3-2 sequence (the maximum value of the magnetic potential sweeps through 1 first, then sweeps through 3, then sweeps through 2), the direction of rotation of the magnetic potential is clockwise, and the motor rotates clockwise.
The simulation in the figure below shows that when the motor rotates counterclockwise, the ABC winding space is arranged counterclockwise. In the simulation results, the back electromotive force relationship is that ACB leads 120°.
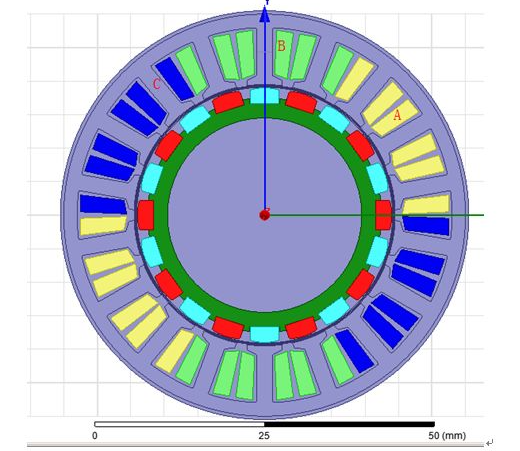
Figure 4 ABC spatial relationship
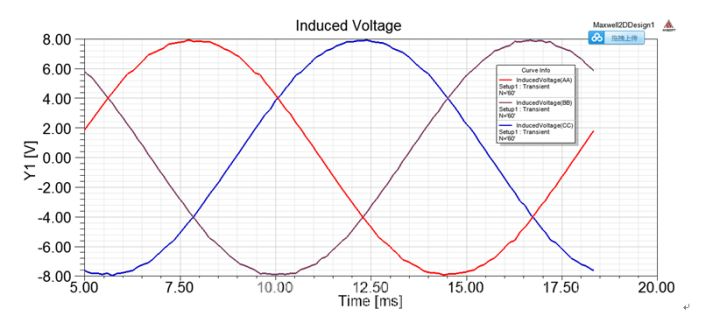
Figure 5 Software calculates back electromotive force phase relationship
1. According to the physical position of the coil (arranged clockwise or counterclockwise), draw the electrical relationship of the three-phase windings based on the phase difference electrical angle, analyze the direction of rotation of the winding magnetomotive force, and then obtain the direction of motor rotation.
2. In fact, there are two situations in the motor: the electrical angle difference is 120° and the electrical angle difference is 240°. If the difference is 120°, the rotation direction is the same as the 123 spatial arrangement direction; if the difference is 240°, the rotation direction is opposite to the 123 winding spatial arrangement direction.


























 XINDA
XINDA