What are the main advantages of permanent magnet motors?
Compared with ordinary three-phase asynchronous motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors have the advantages of high starting torque, short starting time and high overload capacity. They can reduce the installed capacity of the equipment drive motor according to the actual shaft power, saving energy while reducing investment in fixed assets.
Permanent magnet synchronous motors are relatively easy to control, with speed determined solely by frequency. They operate smoothly and reliably, independent of load and voltage fluctuations. The motor's strictly synchronized speed gives it excellent dynamic response, making it particularly well-suited for variable frequency control.
The advantages of permanent magnet synchronous motors lie in their two lows and two highs, namely low loss and temperature rise, and high power factor and efficiency. This is exactly what people pursue for motor performance, which determines the market application position of permanent magnet motors.
Since the magnetic field of the permanent magnet synchronous motor is generated by permanent magnets, the excitation loss caused by generating the magnetic field through excitation current is avoided, which is what we call copper loss; when the motor is running, the rotor runs without current, which significantly reduces the temperature rise of the motor. According to incomplete statistics, under the same load conditions, the temperature rise will be about 20K lower.

Compared with asynchronous motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors have much higher efficiency values under light loads. Their high-efficiency operating range is wide, and their efficiency is greater than 90% when the load rate is in the range of 25% to 120%. The rated efficiency of permanent magnet synchronous motors can reach the current national standard Level 1 energy efficiency requirements. This is their biggest advantage in energy saving compared to asynchronous motors.
In actual operation, electric motors rarely run at full power when driving loads. This is due to two reasons: first, when selecting motors, designers typically determine motor power based on the load's extreme operating conditions, which rarely occur. Furthermore, to prevent motor burnout under abnormal operating conditions, motor manufacturers often include a power margin in the design. Furthermore, to ensure motor reliability, motor manufacturers typically add a certain power margin beyond the user's required power. As a result, most motors in actual operation operate below 70% of their rated power, especially when driving loads such as fans or pumps, which typically operate in the light-load range. While asynchronous motors have very low light-load efficiency, permanent-magnet synchronous motors maintain high efficiency even in this light-load range.
Permanent magnet synchronous motors have a high power factor, independent of the number of motor stages. At full load, the power factor approaches unity. This results in lower motor currents than asynchronous motors, resulting in lower stator copper losses and higher efficiency. However, the power factor of asynchronous motors decreases as the number of motor stages increases. Furthermore, because of the high power factor of permanent magnet synchronous motors, the capacity of the power supply (transformer) supporting the motor can theoretically be reduced, which can also reduce the specifications of the supporting switchgear and cables.
Permanent magnet synchronous motors also have disadvantages. For example, their starting current is approximately nine times greater than that of asynchronous motors. Furthermore, they cannot be started using reduced voltage. Under reduced voltage power supply conditions, their asynchronous starting torque drops more than that of asynchronous motors, making starting difficult. Parameters for the self-starting characteristics and feedback current during system short-circuits of permanent magnet synchronous motors vary significantly among manufacturers. Furthermore, due to the difficulty in obtaining relevant data, the use of permanent magnet synchronous motors introduces uncertainties in the short-circuit level of power systems and starting calculation verification.
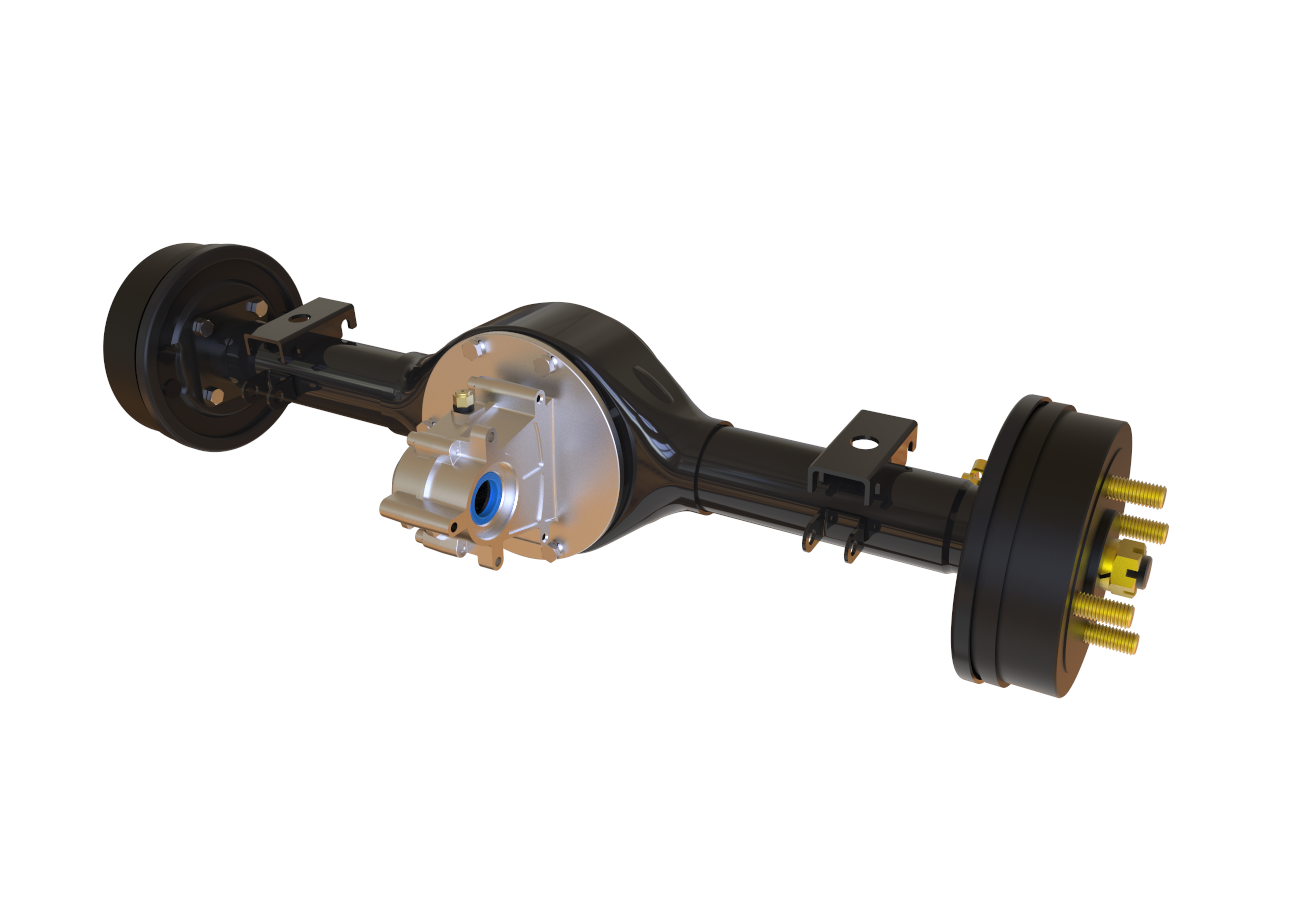
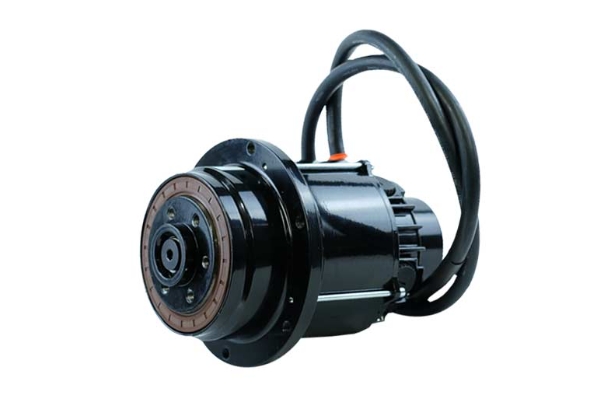
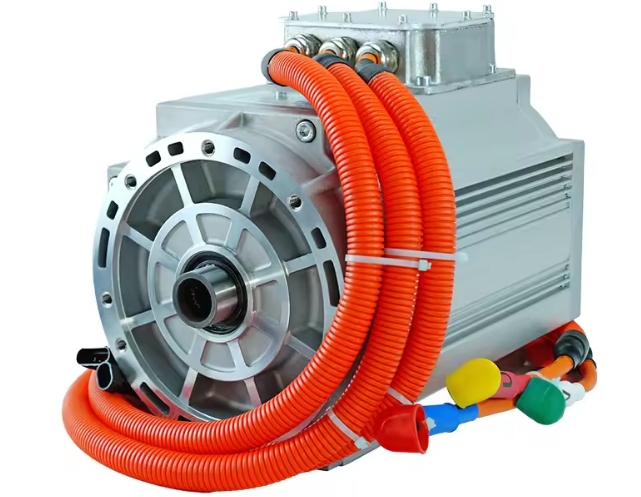
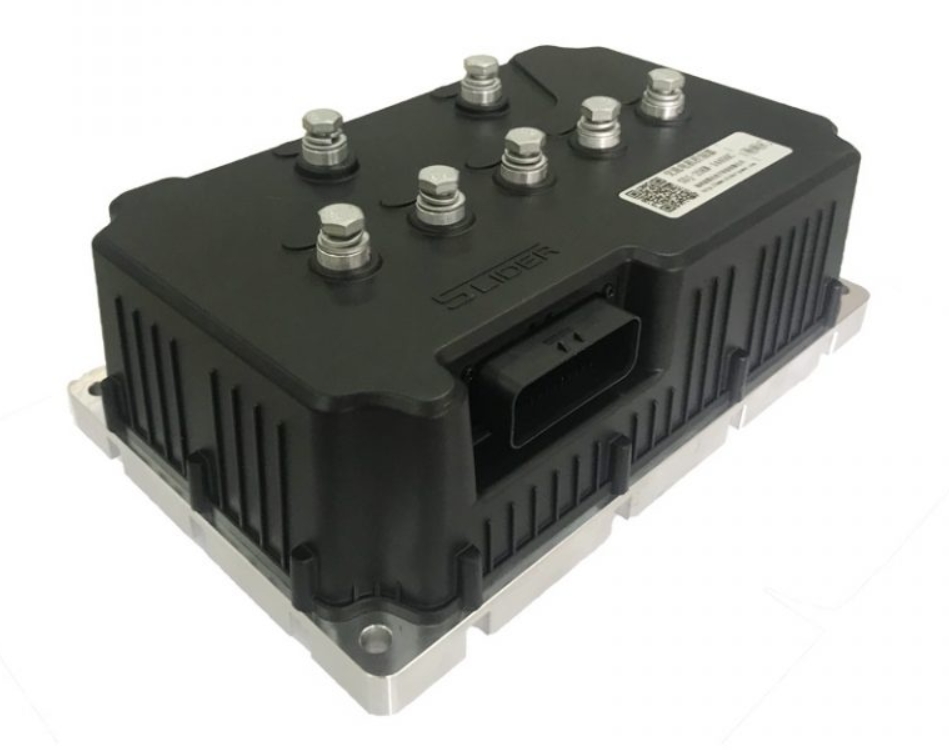


























 XINDA
XINDA