Gear Motor Selection Guide - Precise Matching for Efficient Operation
I. Precise Selection, Embarking on a Journey of High-Efficiency Power
In the field of industrial automation, geared motors serve as core transmission devices, and their performance directly affects the operating efficiency and stability of the entire system. Correct selection is like tailoring a perfect "power armor" for your equipment, ensuring its efficient and stable operation. Below, we'll take a closer look at the key points for selecting geared motors.
Selection Guide
Define requirements
Part 1
Before selecting a geared motor, it is essential to clarify its application scenario, required speed range, torque requirements, accuracy requirements, operating environment (such as temperature, humidity, dust, etc.), and installation method. Only by clearly understanding these requirements can we provide accurate direction for the subsequent selection process.

Part 2
Calculate load parameters
Select motor type
Part 3
Part 4
Determine the reduction ratio
Verification power
Part 5
Part 6
Consider other factors
II. Different types, each displaying its unique abilities
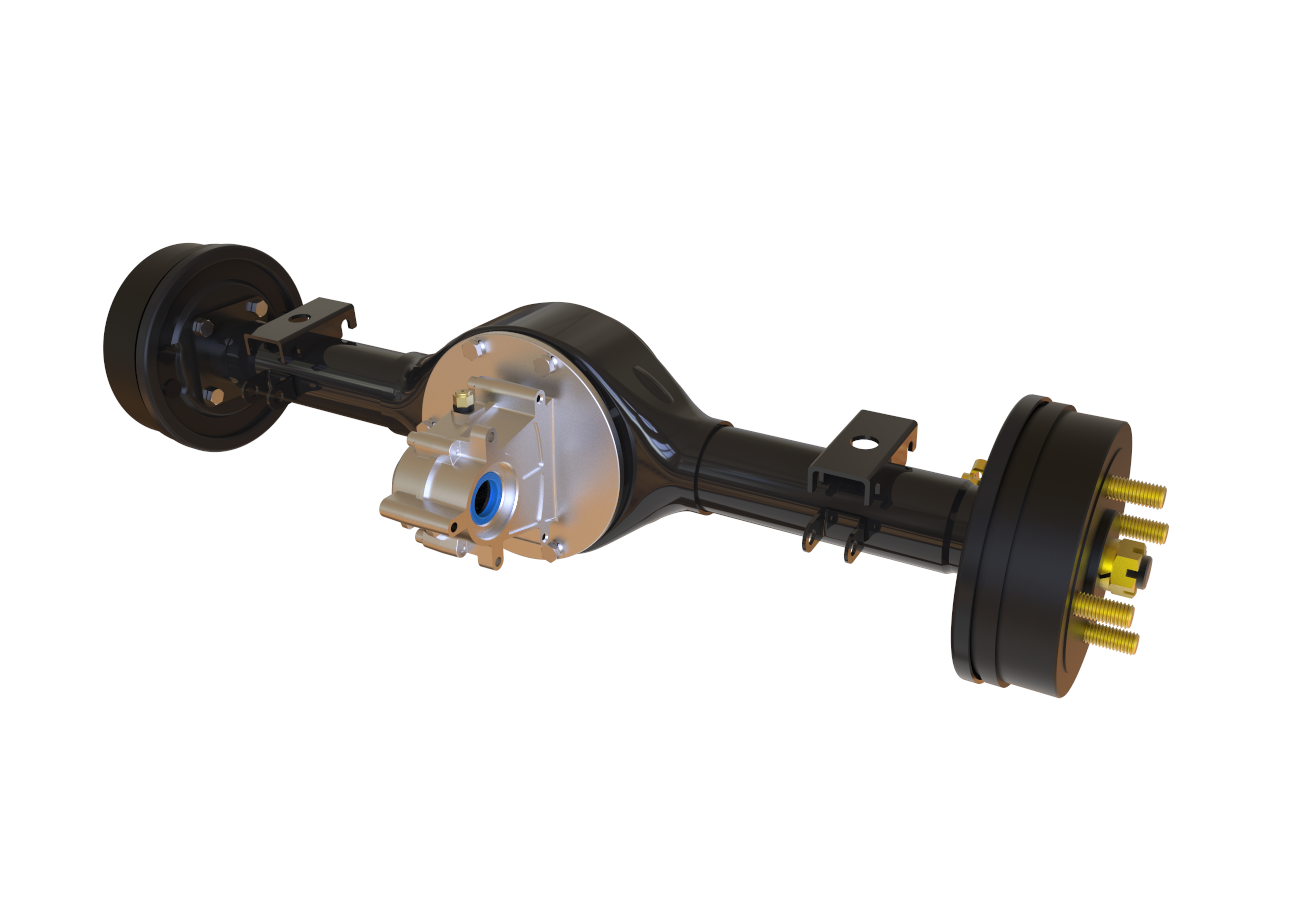
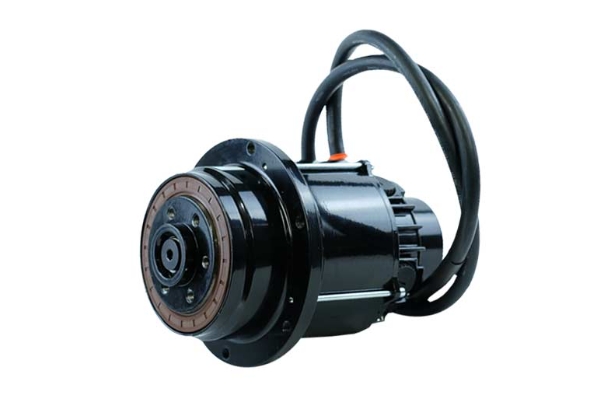
Gear motor
Different types of geared motors perform well in different application scenarios, each demonstrating its unique strengths and contributing to the development of various industries.
For example, planetary gear reducers, with their advantages of high precision, high torque, and high efficiency, are widely used in fields with high precision and performance requirements, such as automated equipment, robots, and CNC machine tools. Worm gear reducers, with their reverse self-locking function and large reduction ratio, play an important role in lifting equipment, conveying equipment, and other applications where load slippage needs to be prevented or a large reduction ratio is required. Harmonic gear reducers, due to their small size, light weight, and high precision, are widely used in industries with extremely demanding space and precision requirements, such as aerospace and medical devices.
In short, there are many types of geared motors, and the selection process is quite complex. However, as long as we consider various factors based on our actual needs, we will definitely be able to select the most suitable geared motor for our equipment. Hopefully, this article will help you gain a deeper understanding of geared motors and make the selection process easier.


























 XINDA
XINDA