![]()
Hello everyone, I am the editor. Today, I will introduce the reasons for the fatigue loss of the geared motor, and the protective measures for the use of the geared motor. The following content is organized by the editor, and the relevant content is for reference.
Various faults will occur when the geared motor is in use, so it is necessary to find these faults and solve them. What should I do when the motor is fatigued and peeled off? The more common ones are pitting peeling, shallow fatigue peeling, and hardened layer peeling.
1. Pockmark fatigue spalling
The technical staff of the gear reducer pointed out that under the action of contact stress, the working surface of the gear is pockmarked and flaky fatigue damage, which is called pitting fatigue spalling. Pitting fatigue spalling is divided into initial pitting (non-extensive) and destructive pitting (extensive). The initial pitting is due to the slight processing error on the tooth surface, the surface is uneven, and the contact is uneven. Under the normal working load of the gear, the stress on the surface is locally higher than the fatigue limit of the material. After a period of cycles, fatigue spalling occurs. Form small pits with a depth of less than 0.1mm and a diameter of less than 1mm. Destructive pits are the secondary cracks generated in the initial pits when the contact stress is large and the number of cycles is large, and develop into spalling pits with a large spalling area and deep pits. The pitting depth is generally less than 0.4mm .
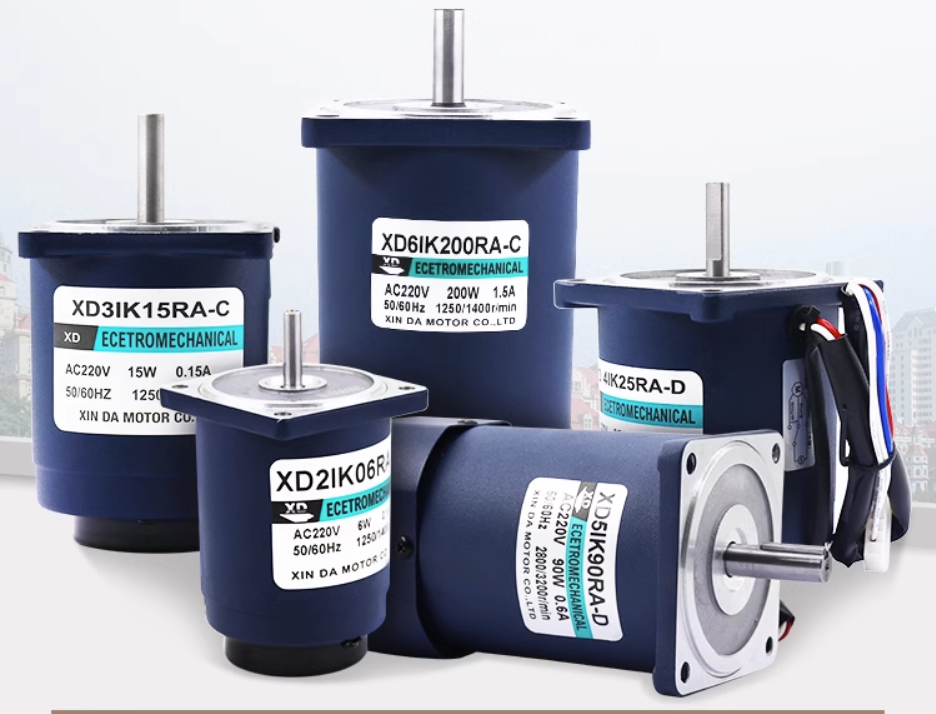
XINDA MOTOR sells gear reducers. Here I will explain to you the formation of pitting and peeling. During the contact process of the rolling belt sliding, the surface of the gear tooth surface is uneven and the surface friction is large. When it is squeezed, the surface is partially covered. Flattening, forming small surface folds, where stress concentration occurs, and local plastic deformation occurs under the action of repeated shear stress, resulting in crack formation. In the case of lubrication, the lubricating oil enters the crack due to capillary action. When the gear moves, the high-pressure oil squeezes into the crack to form an oil wedge. Under the repeated alternating impact of the oil wedge pressure, the crack further expands, and at the same time, the top of the crack is subjected to vertical bending stress, like a cantilever beam, and finally the block is bent to form pitting and peeling off.
It can be seen that the pitting spalling is a crack generated from the surface, and the shallow spalling is caused by the pressure of the oil wedge.
2. Shallow fatigue spalling
The contact fatigue spalling damage that is larger and deeper than pit spalling is called shallow fatigue spalling, which is scale-like, and the pit is usually about 0.4mm deep, but within the depth of the hardened layer. This spalling often occurs where the gear surface roughness is low and the relative friction is small.
3. Fatigue spalling of the hardened layer
The gears that have undergone surface strengthening treatment have large spalling during the working process, and the depth reaches the transition to the hardened layer, which is called fatigue spalling of the hardened layer. It is a form of severe spalling of case hardened gears. Soft tooth surfaces are not prone to such damage.
Protective measures for the use of geared motors
1. Gear meshing transmission protection for geared motors. In gearing systems, straight, helical, bevel, and worm gears are each dangerous. The vast majority of gear transmission equipment adopts fully enclosed protective devices, such as gear reducers, worm gear reducers and common geared motors of various machine tools. But there will also be some gears exposed outside the machine, which will also cause harm to people. Therefore, it is necessary to install a protective cover on the gear exposed outside the machine. The protective cover is basically welded with iron plates in the market. Its shape should be roughly the same as that of the transmission device. The installation should be firm and reliable. The shape should be smooth and beautiful without sharp corners. It should be convenient for future switch, repair and maintenance.
2. Belt drive. Belt transmission is relatively stable among all transmission types, and its characteristics of low noise, simple structure and overload prevention are widely used in daily life and production. However, since the belt rotates at high speed, it is easy to generate frictional electricity and discharge, so the belt drive should not be used in places prone to flammability and explosion. The place where the belt drive must be paid attention to is the place where the belt enters the pulley and the joint of the flat belt. Therefore, the belt drive mechanism used on the general machine must be equipped with a belt guard. For large and high-speed belts that are more than 2m above the ground in the air Take protective measures. Generally, the belt protective cover is mostly made of thin iron plate, and the card should be firmly installed to prevent vibration from falling off. When using the belt, pay attention to the fastening of the joint and the appropriate tightness to prevent disconnection.
3. Protect the coupling device. Blue discs, keys, pins and connecting bolts that rotate at high speed and protrude from the shaft are all hazards and often cause direct injury to people by twisting clothing. Therefore, measures such as countersunk screws, safety couplings without protruding parts and cylindrical guards are required to ensure safe transmission.



























 XINDA
XINDA