![]()
Industrial motors refer to power machinery for industrial production for the purpose of industrial production activities. In China, motors are generally called electrical machinery, which are mainly used to drive various mechanical equipment. According to the purpose, industrial motors can be divided into three categories: general motors and special motors; according to the structure, they can be divided into squirrel cage asynchronous motors, synchronous motors, rare earth permanent magnet synchronous motors, etc. Industrial motors can be divided into DC motors and AC synchronous motors according to the driving mode. According to the electromagnetic design, it can be divided into induction asynchronous motor and DC brushed motor. Induction asynchronous motor is also called squirrel cage motor or three-phase asynchronous motor. Its main purpose is to generate mechanical work or electric energy, which is used in various fields of industrial production and people's life, such as machinery manufacturing, petrochemical industry, textile industry, metallurgy, construction, etc. From the purpose, it can be divided into two categories: general-purpose motors and special-purpose motors. General-purpose motors refer to general-purpose motors, such as textile machinery, small tractors, etc.; special-purpose motors refer to motors designed and manufactured for certain special purposes, such as various special motors used in metallurgy, chemical and other industries Centrifugal pump motors in the petrochemical industry, etc. Classified according to the way of use, it can be divided into two categories: DC motors and AC motors. The stator of a DC motor has windings, the rotor is an iron core, and has no rotating parts; the stator of an AC motor has windings, and the rotor has rotating parts.
There are three types of motors commonly used in industrial production: asynchronous motors, synchronous motors and induction motors. These three types of motors are basically the same in structure, but have different uses. The following is an introduction to the characteristics of asynchronous motors and synchronous motors.
overview
Asynchronous motor: It uses a single-phase asynchronous motor as the prime mover, and rotates through the interaction between the rotating magnetic field and the rotating rotor, and changes the rotor speed by changing the frequency of the rotor current, thereby realizing variable speed and speed regulation. Asynchronous motors have devices such as autotransformers, electromagnetic clutches and hydraulic couplings.
working principle
The synchronous motor is made by using the principle of electromagnetic field. Its stator winding forms a closed magnetic field in space, and since the rotor rotates, it forms a rotating magnetic field in space. When the rotor is energized, a current is generated in the magnetic field. Synchronous motors are operated by electromagnets.The principle of asynchronous motor is different from that of synchronous motor. It is driven by the rotor being attracted by the magnetic field. Therefore, it has the disadvantages of being unable to start and taking a long time to start. However, the structure of the asynchronous motor is relatively simple, and the maintenance is more convenient; while the synchronous motor is much more complicated, not only requires frequent maintenance, but also frequently replaces the coil and iron core. Because asynchronous motors are superior to synchronous motors in terms of performance and price, they still play an important role in industrial production.
performance parameter
The performance parameters of asynchronous motors mainly include four aspects of power, voltage, frequency and speed, and the performance parameters of synchronous motors mainly include four aspects of power and speed.The power of the motor refers to the ability of the motor to generate mechanical work. For example, the power of a 1000W asynchronous motor is 1100W. The motor works at the rated working voltage, and its output power is equal to the power of the motor generating mechanical work plus the mechanical loss and electrical energy loss of the motor, and its efficiency is also equal to the ratio of the efficiency to the input power. Therefore, the ratio of the total electric energy output by the motor to the total electric energy input when the motor is working is called the power factor.
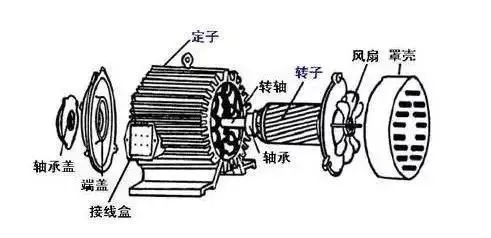
Structural features
1. Asynchronous motors are generally designed and manufactured according to the structural form of three-phase asynchronous motors, and their bases generally adopt the iron core tile type. The rotor is generally of the squirrel-cage type. In order to avoid a short circuit between the rotor and the stator during operation, a rotor overcurrent protection device should be designed on the rotor, that is, a winding overcurrent protection device should be installed between the stator winding and the rotor winding.3. Induction motors can be divided into induction motors and electric excitation motors according to their working principles. Induction motors are divided into two types: single-phase induction motors and three-phase induction motors, which are quite different in terms of structure, operation mode and performance.
main feature
1. The structure of the asynchronous motor is simple, easy to manufacture, cheap, and easy to use and maintain.2. The synchronous motor has a high power density, and its weight is only half of that of the asynchronous motor.3. Synchronous motors have slightly higher efficiency than asynchronous motors.4. The vibration of synchronous motor is smaller than that of asynchronous motor.5. The synchronous motor can run stably within a certain frequency range.6. The synchronous motor does not run intermittently (that is, no-load), and there is no inrush current when starting.
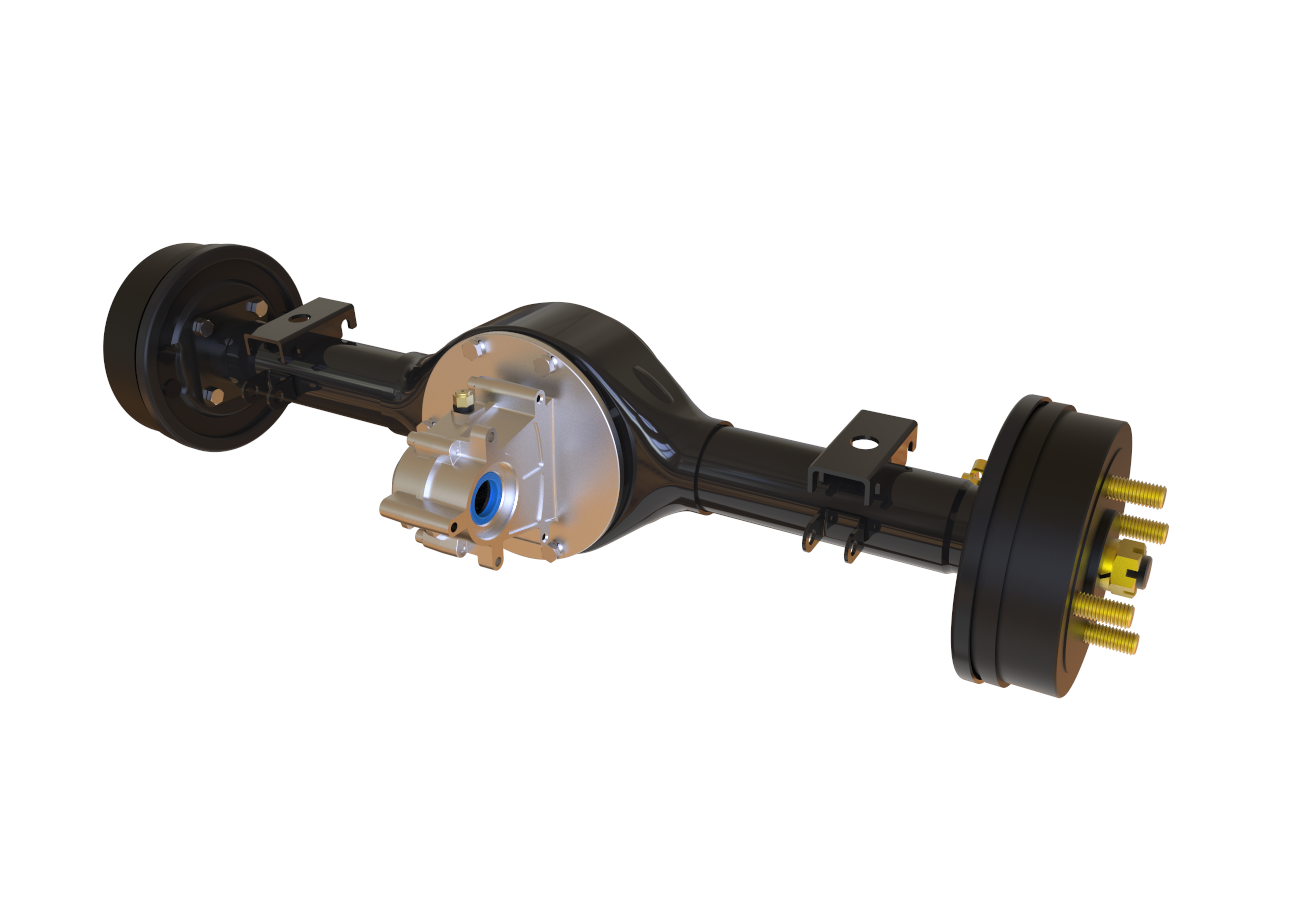
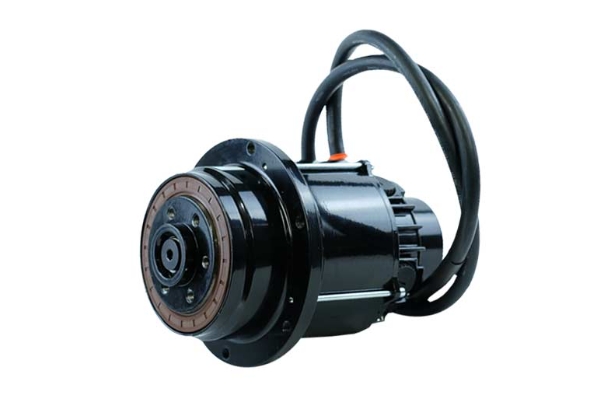
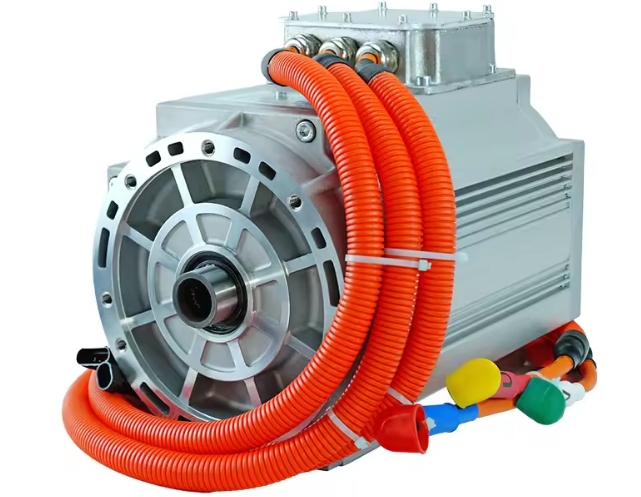
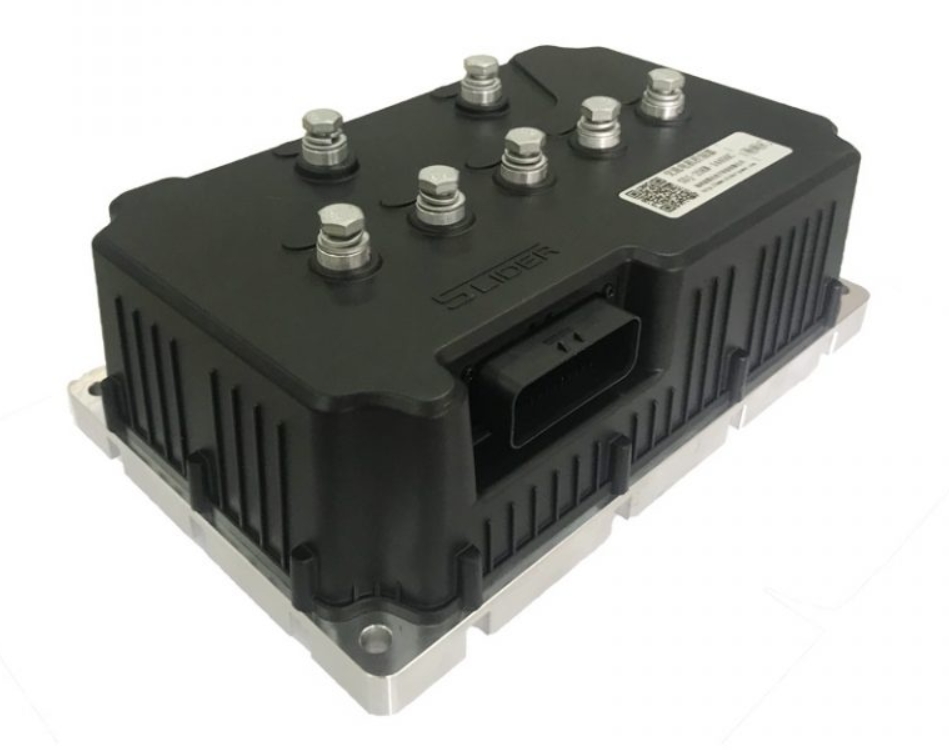


























 XINDA
XINDA